Facts and Figures in Maintenance and Repair

Maintenance is a key factor determining manufacturers’ success since it ensures preferably smooth operation. At the same time service and repair are significant cost factors. We wanted to get a more detailed picture and started researching. Some of the most relevant findings:
Both direct and indirect costs vary from company to company. Estimates range from 10 to 40 percent depending on industry and type of plant. In 2011 a consultants’ study has even calculated that
‟up to 60 percent of production costs can be affected directly and indirectly by the efficiency of maintenance performance.”
acatech published absolute figures in 2015:
‟By avoiding three to five times higher follow-up costs in case of a failure, maintenance generates plant availability and productivity values for German industry with an equivalent of approximately one trillion Euros per year.”
A survey by Becker und Brinkmann among 60 companies shows for large-scale plants:
- For 50 percent a dedicated department was responsible for maintenance.
- For 45 percent tasks were allocated to different departments, such as production and workshop.
- For 5 percent production or plant operation were solely in charge for maintenance.
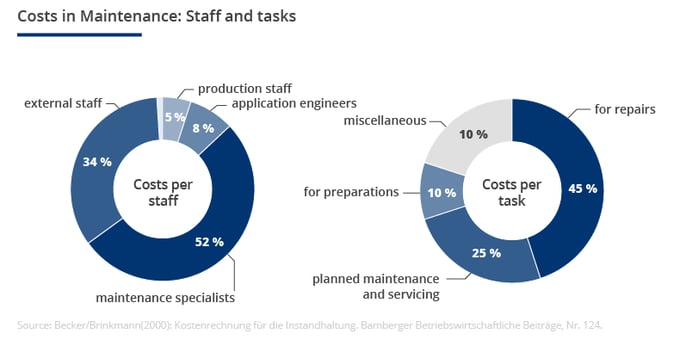
Chart: Costs in maintenance and repair per staff group and task.
Becker and Brinkmann assume:
‟The relatively high percentage of nearly 10 % for work preparation indicates that maintenance should be classified as function requiring intensive coordination and increased need for information.”
With technological and operational developments, requirements on maintenance change and evolve as well. For those who want to read more about this, the position paper of acatech is recommended (English version available).
Glossary: all about maintenance
Maintenance
Maintenance includes all measures to preserve the target condition and therefore to prevent damages. Maintenance serves to extend the lifetime of plants. Ideally, all work steps are documented in maintenance schedules.
Typical maintenance work includes: cleaning, lubrication, replacing and adding auxiliaries, setting and adjustment.
Inspection
Inspection is defined as examining and evaluating the wear of parts, components and equipment comparing actual values with nominal values. Inspections are carried out in defined, regular intervals. The frequency of such inspections depends on environmental impacts / influences, expected damages and machine utilization.
Inspections include: noise testing, visual inspection on wear marks, wear measurements, check of bolted connections, corrosion tests.
Repair
Repair is maintaining or restoring the functionality by replacing or repairing parts. Repair serves to maintain the operational and functional reliability as well as to ensure perfect operational performance of machines and aggregates.
Repair includes: replacement of parts to avoid damages or to restore functionality.


Comment